ESA Press Release “Unusual carbon balance at Mars explained by sunlight, finds ExoMars”
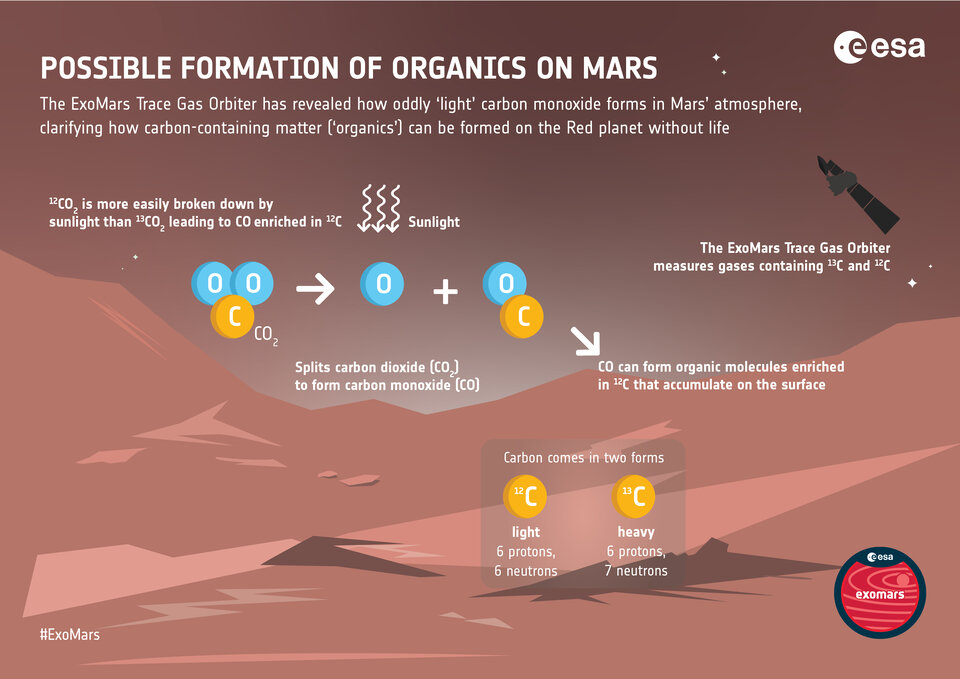
A research team led by Professor Shohei Aoki of the Department of Complex Science and Engineering, Graduate School of Frontier Sciences at the University of Tokyo and Project Researcher Tatsuya Yoshida of this laboratory has revealed that carbon monoxide in the Martian atmosphere is low in carbon-13*1 using observation data from the European Mars Explorer ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter This is the main component of the Martian atmosphere. This is thought to be because carbon 12 is more selectively destroyed when carbon dioxide, the main component of the Martian atmosphere, is decomposed into carbon monoxide by solar radiation. Organic matter found on the Martian surface also lacks carbon-13, suggesting that atmospheric photochemistry may have played an important role in the process of organic matter production. Dr. Yoshida predicted that carbon monoxide in the Martian atmosphere is low in carbon-13 using an atmospheric model, and contributed to showing that the results of this analysis are consistent with the theory.
1 Carbon-13: A stable isotope of carbon with one more neutron than the usual carbon-12.
ESA press release
“Unusual carbon balance at Mars explained by sunlight and chemistry, finds ExoMars”
Reference
1. Aoki, S., Shiobara, K., Yoshida, N., Trompet, L., Yoshida, T., Terada, N., … & Ueno, Y. (2023). Depletion of 13C in CO in the Atmosphere of Mars Suggested by ExoMars-TGO/NOMAD Observations. The Planetary Science Journal, 4(5), 97.
(https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.3847/PSJ/acd32f/meta)
2. Yoshida, T., Aoki, S., Ueno, Y., Terada, N., Nakamura, Y., Shiobara, K., … & Koyama, S. (2023). Strong Depletion of 13C in CO Induced by Photolysis of CO2 in the Martian Atmosphere, Calculated by a Photochemical Model. The Planetary Science Journal, 4(3), 53.
(https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.3847/PSJ/acc030/meta)


