Research
投稿数17件Today, Mars has 0.006 atm thin atmosphere, on the other hand, 4 billion years ago it had ticker atmosphere, with the pressure of over 5 atm. (Kurokawa et al., 2017). ” Where and how was the ancient thick Martian atmosphere lost? “ and ” What is it like today ? “ are the important topics in the Martian research. The ratios of isotopes are considered significant parameters in comprehending the indications of atmospheric evolution and circulation, as they change only by limited processes. The current Martian atmosphere consists mostly of CO2, accounting for over 95%, and the...
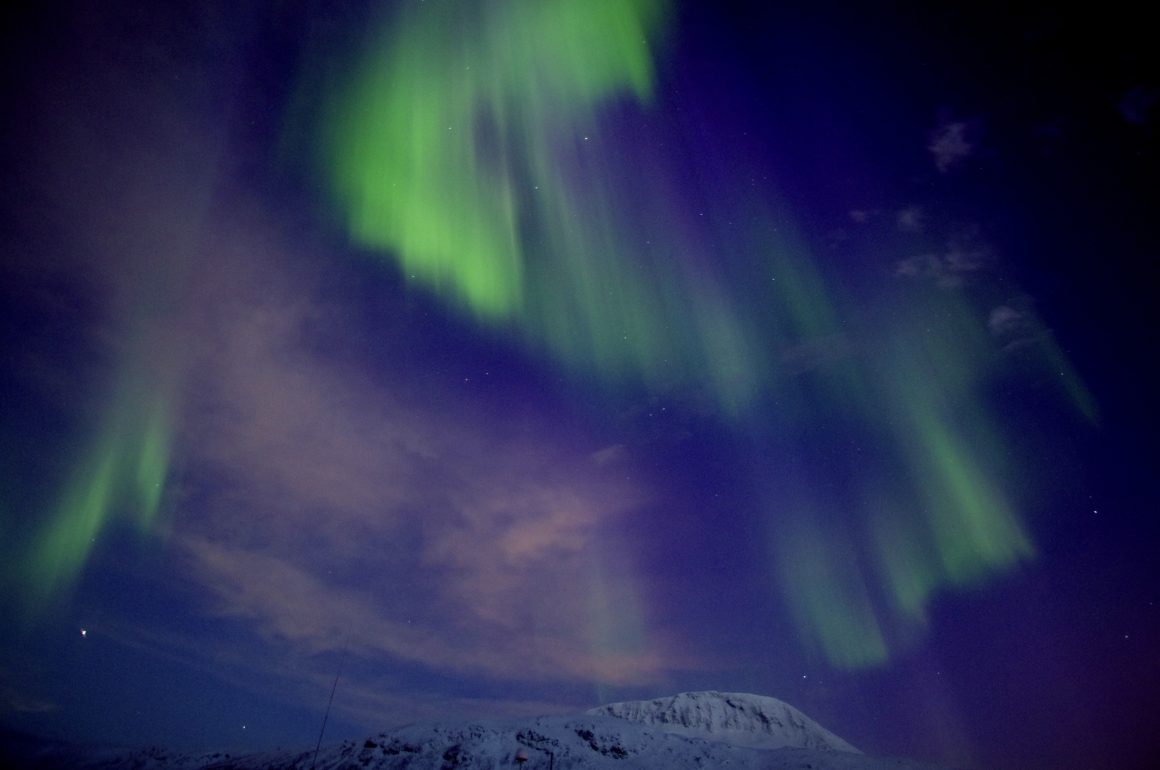
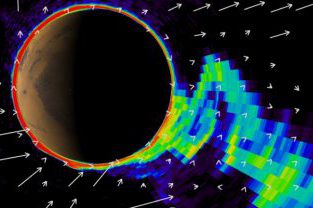
(*top picture of “Earth” aurorae taken by Prof. Hitoshi Fujiwara at Svalbard islands) Fig1. Diffuse aurora on Mars to cover whole nightside disk when the solar energetic particle (SEP) encountering on Mars at the (left) start and (right) peak of the September 2017 [Schneider et al., GRL, 2018]. Have you ever seen the Martian aurora? The U.S. Mars MAVEN spacecraft recently discovered Mars’ unique aurora covering the entire night side of the planet (Schneider et al., GRL, 2018), and the latest Arab Mars EMM spacecraft has discovered many more types of Mars aurora (Lillis et al., GRL, 2022). Auroral images...
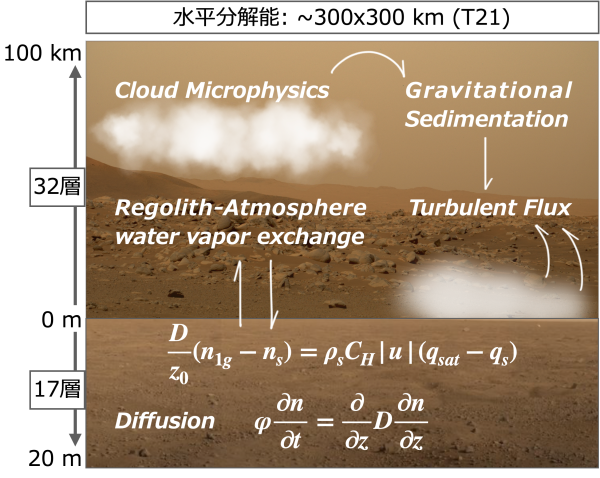
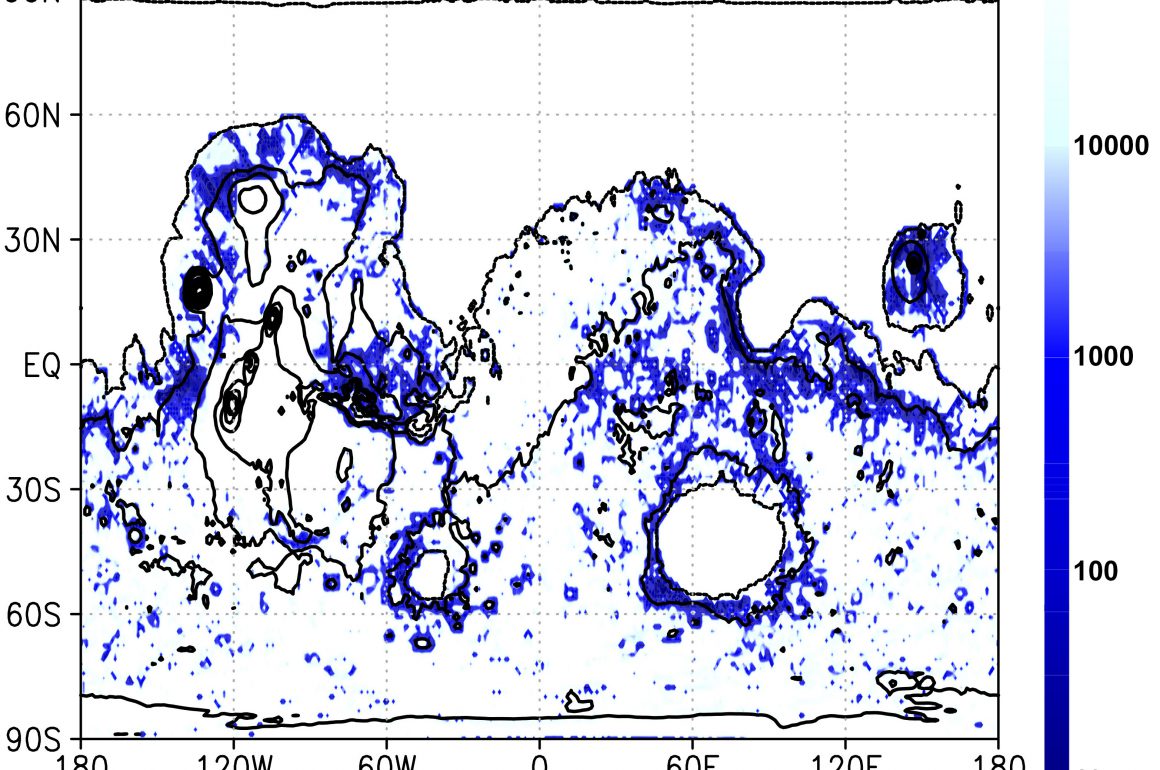
Have you ever seen what the surface of Mars looks like as photographed by a spacecraft? The Martian surface is like a desert environment, covered with grains of sand called “regolith”. Mars regolith is a porous material with many voids, and it is known to adsorb water vapor on its surface and store ice in its pores. NASA/JPL-Caltech/ASU/MSSS Recent studies have revealed that water in the regolith is released into the atmosphere during the day and stored underground at night. However, the extent to which this phenomenon affects the Martian water cycle is not yet well understood. It is also...
(Development of the plasma wave receiver equipped with JUICE) One of the roles of Staff is to make a long-term investment, i.e., to work hard on tasks that do not produce immediate results. With your help, we have been responsible for the development of the following projects, especially the electric and radio wave observation equipment and data processors. – Hisaki / Exceed (launched successfully in September 2013! On going) – Geospace explorer ERG (launched in 2016) – BepiColombo (launched in 2017,scheduled for 2024-2026 in orbits) – ESA JUICE (launch in 2022,scheduled for 2029-2031 in orbits) In parallel, he is participating...
Atmospheric and electromagnetic phenomena on the planet vary dynamically on various timescales and must be observed continuously for long periods to understand them. However, large telescopes such as Subaru Telescope are generally open for public, which makes it difficult to make continuous observations for long periods. We have been developing a unique observation network by installing state-of-the-art instruments in our own observational facilities, which are capable of continuously monitoring planets. In 1985, our laboratory developed the infrared heterodyne spectrometer, and it has been useful for the study of the Earth’s atmosphere such as ozone. In recent years, in collaboration with...
The solar wind and solar EUV radiation stripe away planetary atmosphere into space. The atmospheric escape phenomenon is not only a compelling subject to study the physical mechanisms themselves, but is also important for understanding the evolution of planetary atmospheres, the diversity of planetary atmospheres, and the conditions under which habitable planets can be established. We have developed electromagnetic hybrid (particle ions/fluid electrons) and magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) simulation codes that comprehensively describe the interaction between the solar wind and the ionosphere of unmagnetized planets. We have been clarifying the physical mechanisms and pathways by which the ionized atmospheres of planetary origin...
On the surface of Mars, there are many “flowing water topographies” (valley networks), which are thought to be traces of liquid water that formed about 3.8 billion years ago. However, the mechanism to maintain the warm climate necessary for their formation is unknown. This is because the Sun at that time was fainter than it is today, and the atmosphere was not sufficiently warmed by a carbon dioxide-rich atmosphere. We have developed a new model of the Martian climate and streamflow based on the Earth’s climate model, and have shown that Mars at that time could have had a cool...
We are developing a full particle simulation model using the DSMC method to study the slow hydrodynamic escape of the atmosphere of an Earth-like planet. Slow hydrodynamic escape is one of the mechanisms of atmospheric escape into space. Proxima b, which are found in the habitable zone around M-type stars, and Trappist-1, e, f, and g, which are found in the habitable zone around M-type stars, may be in a slow hydrodynamic escape state. They are also thought to have occurred on Earth and Mars in the early days of formation. The amount of atmosphere escaping by slow hydrodynamic escape...
Solar Energetic Particles (SEPs) are electrons, protons, and heavy ions with energies ranging from a few keV to a few GeV that are ejected by solar flares and coronal mass ejections, and they propagate through interplanetary space and descend into planetary atmospheres, causing ionization, dissociation, and heating of atmospheric molecules. When a large SEP event occurs, the dissociation of oxygen and nitrogen molecules in the polar regions of the Earth increases NOx and HOx, and ozone is reduced by about 50%. In contrast to Earth, where the effects of SEPs on the atmosphere have been well studied by both observation...
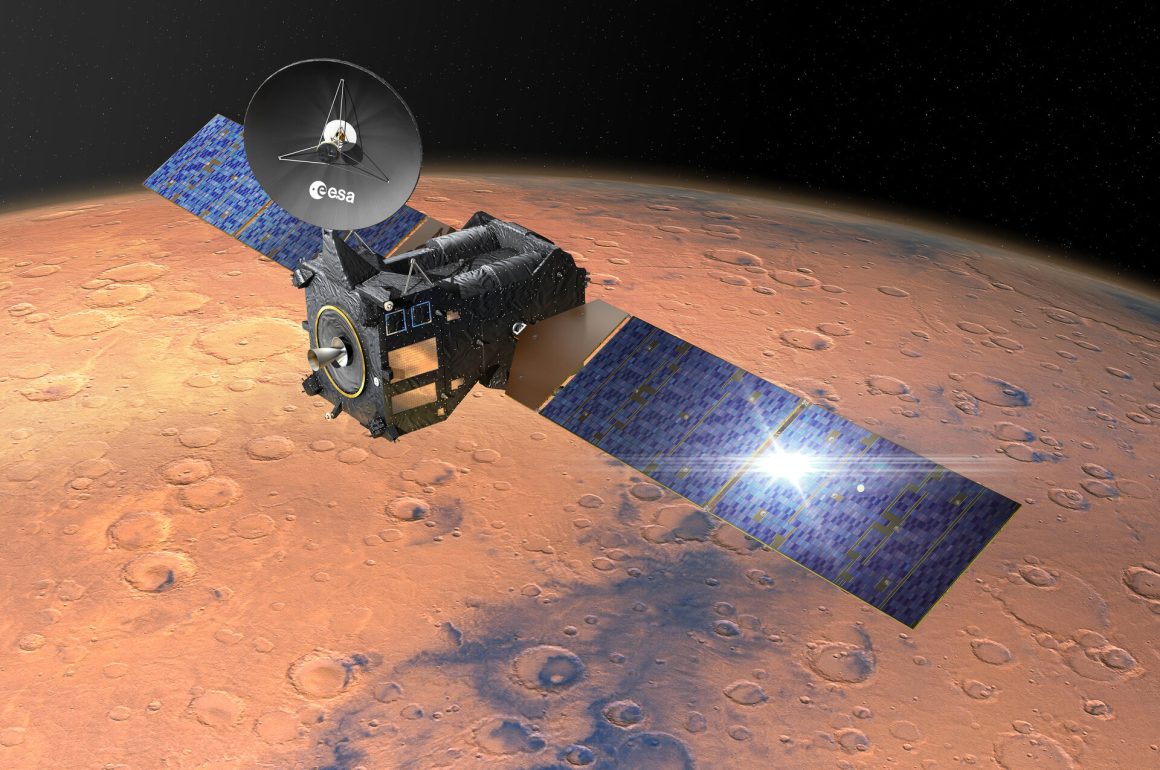
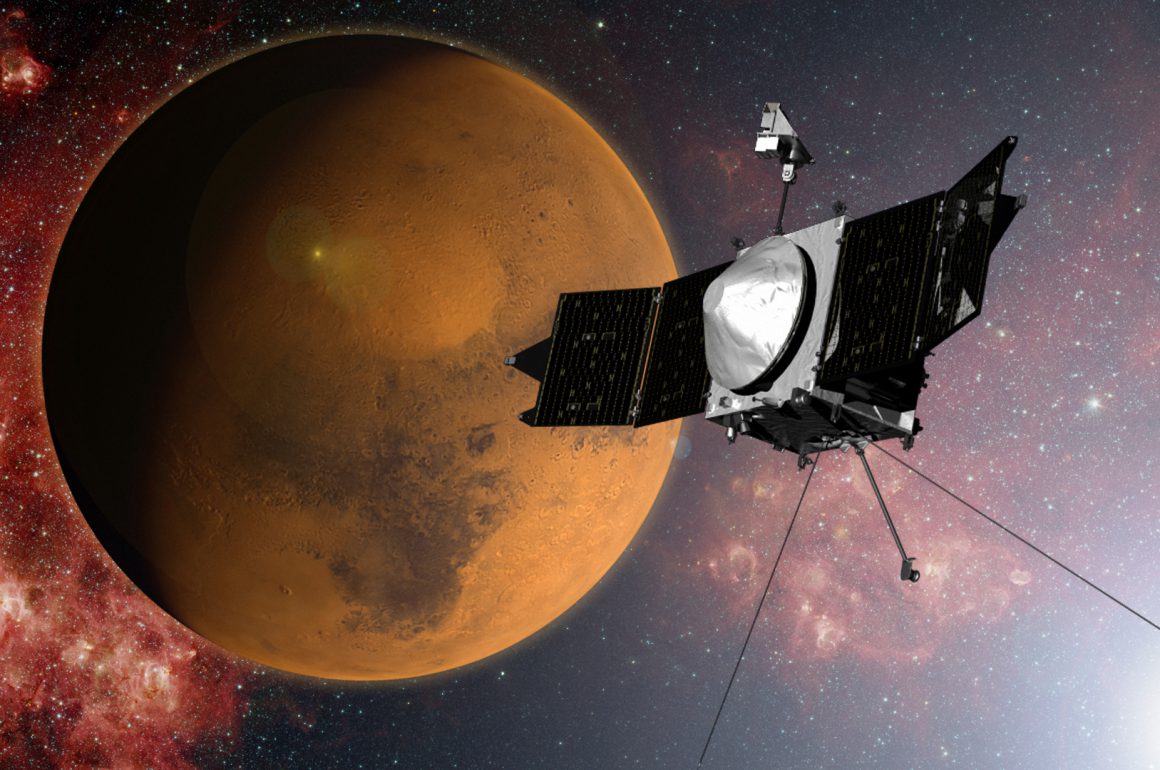
By escaping from the atmosphere and exploring planets in space, we can obtain valuable data that cannot be obtained from the ground. Our group has been involved in more than 16 space exploration missions including JIKIKEN, Akebono, Geotail, Nozomi, Kaguya, Reimei, AKATSUKI, HISAKI, MAVEN, TGO, BeppiColombo, MMX, and JUICE, and have a lot of great experients of international and domestic collaborations. We have been exploring the unknown with world-wide teamwork. We have recently investigated the ionospheric escape by the NASA’s MAVEN spacecraft, and vertical coupling and water cycle in the Martian atmosphere by the ESA’s TGO spacecraft. We are also...
more
Archives
Tags
INFORMATION
Entrace Exam. info.
Do not hesitate to contact and freely visit our lab
Lab Booklet:
Dep. Booklet:
Entrace Exam. also found in Department of Geophysics web page